The race to create seamless mobile experiences is redefining how modern applications are built. Businesses now operate in ecosystems filled with countless devices, platforms, and user expectations. Each interaction must be fast, consistent, and accessible.
The scale of this shift is clear. According to Statista, the global mobile app market is projected to exceed $613 billion by 2030, driven by faster deployment cycles and the growing adoption of hybrid and cross-platform frameworks. This marks a deeper transformation as development is no longer a choice between web and native, but a blend of both to achieve efficiency and scalability.
Hybrid app development captures that balance. It merges native performance with web flexibility through a shared codebase and unified architecture. The outcome is faster releases, easier maintenance, and consistent performance across platforms, without sacrificing user experience.
This guide breaks down the fundamentals of hybrid app development, how it differs from native and cross-platform models, and why it has become central to enterprise mobility strategies.
What is Hybrid App Development?
Create once and deliver everywhere
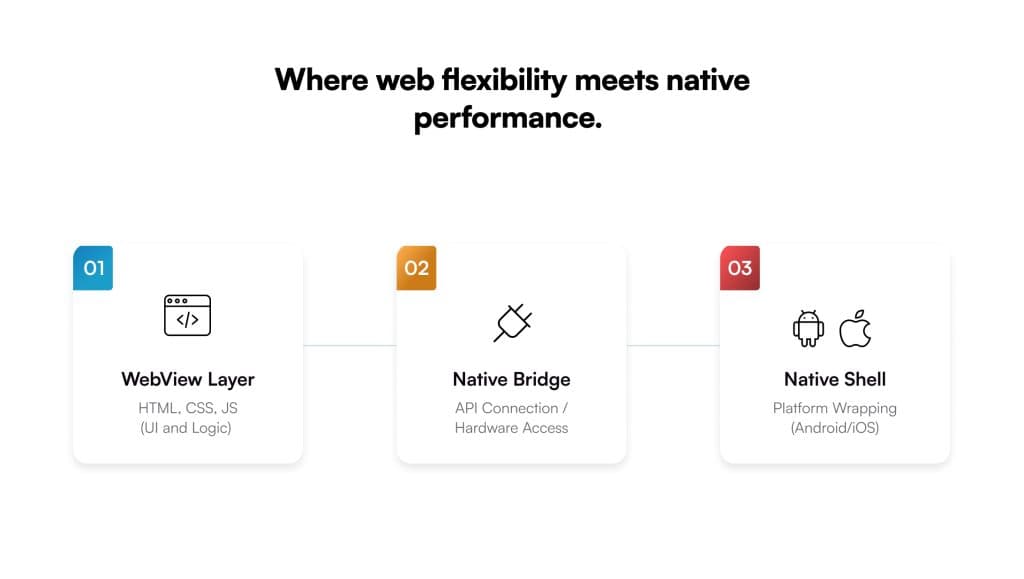
Hybrid mobile app development uses one codebase to create apps that run on both Android and iOS. The goal is simple:
- Reduce effort
- Increase reach
- Keep performance close to native
At its core, a hybrid app runs inside a native shell. The shell connects the web code to the device. Inside it, a WebView layer renders the interface and bridges access to hardware features like camera or GPS. Everything feels native to the user, even though much of the app is powered by web technologies underneath.
Developers build these apps using HTML5, CSS, and JavaScript, supported by frameworks like React Native, Flutter, Ionic, and Xamarin. Each framework brings its own strengths — some favor performance, others speed or flexibility.
Native vs. Hybrid Mobile App Development
| Factor | Native App Development | Hybrid App Development |
| Codebase | Separate codebases for each platform (iOS, Android) | Single codebase for all platforms |
| Performance | Highest, optimized for specific OS | Near-native, slightly lower for complex tasks |
| Development Time | Longer — separate builds and testing | Shorter — shared development and faster releases |
| Maintenance | Complex — dual updates and bug fixes | Easier — one update for all platforms |
| Access to Hardware | Full access to device features | Partial, via plugins or APIs through WebView |
| UI Consistency | Tailored for each platform | Uniform design across platforms |
| Scalability | High, but resource-intensive | High, with faster iteration cycles |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial and maintenance cost | Lower upfront and lifecycle cost |
Once you start planning your mobile app, the first decision you face is how to build it. Native or hybrid. Both deliver apps. But they take very different paths to get there.
Native mobile app development builds separate apps for each platform. Swift for iOS. Kotlin or Java for Android. It gives complete access to device hardware, delivers the best performance, and offers fine control over UI. The trade-off is cost and time. Two teams. Two codebases. Two release cycles. Every update doubles the effort.
Hybrid mobile app development takes a more unified route. It uses one codebase wrapped inside a native shell, making it run across platforms. The app feels native but draws its interface from web code through a WebView layer. Development is faster, updates are simpler, and the overall cost stays lower.
Performance is close to native for most use cases. The gap may show only in high-intensity applications like heavy gaming, advanced graphics, or hardware-dependent tasks. That’s where native still makes sense.
For everything eCommerce, enterprise dashboards, banking, logistics, healthcare apps hybrid strikes the right balance.
Explaining the Hybrid App Development Frameworks
Write once, run anywhere.
Hybrid app development connects web code with native device features.
The architecture is layered. At the top sits the WebView, where HTML, CSS, and JavaScript render the interface. Beneath it lies the Native Bridge, the layer that lets web components talk to device hardware — camera, GPS, storage, and sensors. Plugins extend this bridge, giving access to native APIs that the browser alone can’t reach. Together, these layers make the app feel and behave like a native one while maintaining the flexibility of the web.
This framework design allows code reusability at scale. Developers build once and reuse the same modules across operating systems. It also supports native API integration, enabling smooth performance and offline access through caching or local storage. The result — faster builds, consistent updates, and fewer moving parts to maintain.
Several frameworks dominate the hybrid ecosystem today, each built with a slightly different purpose. Each brings its own balance of performance, flexibility, and ecosystem support. The choice depends on what matters more, be it UI fluidity, team skill set, or integration depth.
Comparison of Leading Hybrid App Development Frameworks
| Framework | Supported Platforms | Ideal Use Case | Community & Support |
| React Native | iOS, Android | Enterprise apps with native-like performance | Strong, active, backed by Meta |
| Flutter | iOS, Android, Web | Design-heavy apps, startups, and enterprise prototypes | Rapidly growing, backed by Google |
| Ionic | iOS, Android, Web, Desktop | Content-driven apps, internal enterprise tools | Large, open-source community |
| Apache Cordova | iOS, Android | Lightweight apps, quick MVPs | Moderate, legacy but stable |
| Xamarin | iOS, Android, Windows | Enterprise systems integrated with .NET | Reliable, backed by Microsoft |
A well-chosen hybrid app development framework does more than simplify code. It accelerates product velocity, strengthens maintainability, and ensures that design and performance scale together. For enterprises balancing speed with structure, it is the foundation that turns hybrid development from an experiment into a long-term strategy.
What are the Benefits of Hybrid App Development?
The benefits of hybrid app development go beyond cost or convenience. They touch speed, scalability, and sustainability that decide how fast a product grows.
- Speed to Market: The first advantage is speed to market. With a single codebase, teams build once and deploy across Android, iOS, and the web. No duplication. No platform lag. This allows faster releases and quicker validation of product ideas.
- Scalability: The second is scalability. Hybrid apps grow easily across markets and devices. The same code adapts to multiple screen sizes and OS versions, reducing dependency on platform-specific rebuilds.
- Maintenance: Maintenance is simpler too. Updates roll out once and reflect everywhere. Bug fixes, version changes, and security patches require less coordination between teams. That translates into lower downtime and smoother operations.
- Offline Capability: Hybrid frameworks also support offline capability through caching and local storage. This ensures access to critical app functions even without network connectivity — a vital feature for enterprise and field applications.
- Cost Efficiency: Then there’s cost efficiency. One development effort means fewer resources, lower testing overhead, and easier maintenance. Over time, this lowers total cost of ownership without compromising user experience.
- Consistency:Finally, consistency. Hybrid apps maintain a uniform design and interaction pattern across platforms. For brands, that means unified identity and predictable user behavior everywhere.
Best Examples of Hybrid Mobile App Development
Some of the most widely used apps today run on hybrid mobile app development platforms. Their success proves that hybrid isn’t a compromise — it’s a strategy built for scale.
Instagram is one of the clearest examples. Built using React Native, it merges web speed with native experience. The shared codebase allows quick feature rollouts and consistent performance across iOS and Android. For a platform handling billions of user interactions daily, that efficiency is critical.
Uber follows a similar model. Its driver and rider apps rely on hybrid frameworks to maintain real-time functionality while managing constant updates. The hybrid layer enables faster iteration cycles, ensuring both apps evolve together without separate rebuilds.
Evernote uses a hybrid structure to manage its multi-device ecosystem. The app’s web foundation keeps note synchronization smooth, while native integrations ensure fast search, camera access, and offline usability.
Amazon Appstore also embraces hybrid architecture to support its massive catalog across devices and regions. The shared core allows Amazon to maintain design consistency, add new features faster, and streamline global deployment.
Each of these brands balances hybrid scalability with native optimization layers. Performance-critical elements — like animations or real-time features — often run on native modules, while hybrid components handle structure, layout, and data flow. The result is a blend that delivers reach without losing responsiveness.
For enterprises, these examples show what hybrid can achieve at scale — faster updates, unified design, and global reach without the complexity of maintaining separate native codebases.
Hybrid isn’t the future of mobile development. It’s already powering it.
Analyzing Hybrid App Development Cost
The cost of hybrid mobile app development is never a flat number. It shifts with structure, complexity, and the depth of integrations behind the interface. Two apps may look similar, but the engineering beneath defines the difference.
Below are the key factors that drive cost — and why understanding them early helps you plan smarter.
Key Cost Drivers
- Framework Selection
The foundation decides performance and cost. Frameworks like React Native and Flutter deliver near-native quality but need experienced developers. Ionic or Cordova work faster for simpler builds but may add effort later if you scale.
- App Complexity
A minimal MVP costs less than an enterprise-grade app. Advanced apps involve multiple modules, user roles, databases, and security layers — all of which raise time and budget.
- Integrations and APIs
Adding payment systems, analytics, CRMs, or push notifications increases build hours. Each integration requires testing and compliance checks, especially in enterprise environments.
- Backend Architecture
A strong backend is essential for speed and scalability. Microservices, caching, and database design all add to engineering time. It’s the backbone that defines how well the app handles growth.
- UI and UX Design
Complex UI elements, animations, or adaptive layouts require more effort. Clean design costs less to build but may offer limited flexibility.
- Deployment and Maintenance
Post-launch costs often exceed initial builds. Hybrid reduces this burden through a single codebase — one update, one QA cycle, one deployment.
Approximate Cost Range by App Type
| App Type | Description | Estimated Cost Range (USD) |
| MVP / Prototype | Basic UI, minimal features, few integrations | $15,000 – $30,000 |
| Mid-Complexity App | Multi-screen, multiple APIs, moderate backend | $30,000 – $70,000 |
| Enterprise-Grade App | Scalable backend, security layers, dashboards | $70,000 – $200,000+ |
| High-Interactivity App | Real-time sync, animations, offline support | $100,000 – $250,000+ |

In-House vs. Offshore Hybrid Mobile Development Team
Building in-house gives direct oversight but comes with higher fixed costs — salaries, management, and infrastructure.
Partnering with an offshore hybrid mobile development team often reduces expenses by 30–50%. It brings specialized expertise, flexible engagement models, and faster turnaround without compromising quality.
Long-Term Value
Hybrid development lowers total ownership cost by consolidating updates and reducing team size. The same codebase powers multiple platforms — simplifying support, versioning, and maintenance across releases.
The real value lies in control — predictable budgets, faster delivery, and scalable growth built on a single, maintainable core.
Partner Galaxy Weblinks for Hybrid App Development
Choosing the right partner defines how well your hybrid strategy performs. The technology may decide speed, but execution decides success.
At Galaxy Weblinks, we offer enterprise-grade hybrid app development services built for scale, stability, and performance. Our teams bring deep technical expertise across leading frameworks like React Native, Flutter, Ionic, and Xamarin, enabling faster builds and consistent cross-platform results.
Every project follows a structured, full-lifecycle approach from architecture design and UI development to integration, testing, and deployment. Our engineering processes emphasize the three pillars of reliable enterprise software:
- Security
- Scalability
- Maintainability
We design hybrid apps that move as fast as your business does. Whether it’s improving time-to-market, streamlining updates, or scaling across platforms, our goal is simple — to help you build once and deliver everywhere.
Discover how our hybrid app solutions can accelerate your product’s journey from concept to scale. Contact us Today!

